Not all red rashes on the head are scalp psoriasis plaques.
Although psoriasis is a common condition, there are similar looking skin conditions that occur on the scalp. Correctly diagnosing the cause of a scalp plaque is important for effective treatment.
Scalp psoriasis
Scalp psoriasis plaques is a common skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is an autoimmune condition that causes skin cells to grow too quickly.
People with psoriasis develop red or brown, scaly plaques, potentially anywhere on the body, but characteristically on the elbows and knees. The affected areas can be itchy and painful.
Psoriasis sometimes involves the scalp with or without lesions on other parts of the skin.
Unlike some of the other rashes that appear on the scalp, scalp psoriasis more often extends beyond the hair line. Scalp psoriasis plaques also tend to have sharp, well-demarcated borders. The scale of psoriasis tends to be thick and silvery.
Unlike many of the other similar looking scalp conditions, psoriasis is associated with an increased risk of arthritis and cadiovascular disease.
Learn more about our services: scalp doctor near me
How to Treat Scalp Psoriasis
There are several treatment options available for scalp psoriasis. The best treatment option for you will depend on the severity of your condition and your overall health. Some of the most common treatment options include:
- Topical Treatments: Topical treatments are applied directly to the affected area of the scalp. They can help reduce inflammation, itching, and scaling. Some common topical treatments for scalp psoriasis include corticosteroids, vitamin D analogs, retinoids, and topical retinoids.
- Phototherapy: Phototherapy involves exposing the affected area to ultraviolet light. This can help reduce inflammation and scaling. Phototherapy can be done in a dermatologist’s office or with a specialized device at home.
- Systemic Medications: Systemic medications are taken orally or by injection. They can help reduce inflammation throughout the body, which can improve scalp psoriasis symptoms. Some common systemic medications for scalp psoriasis include methotrexate, cyclosporine, systemic retinoids and biologics.
Does Psoriasis Cause Hair Loss?
Any severe skin inflammation on the scalp, including psoriasis, can cause hair loss.
The hair loss is usually temporary and will grow back once the condition is under control. However, if the inflammation is severe, in some cases, the alopecia may be permanent.
Psoriatic Arthritis and Scalp Psoriasis
One of the reasons it is important to know the difference between scalp psoriasis and other scalp conditions is the associated diseases.
People with scalp psoriasis are almost 4 times more likely to develop psoriatic arthritis versus people with psoriasis without scalp involvement. Psoriatic arthritis is a type of inflammatory arthritis that is associated with psoriasis. According to the National Psoriasis Foundation, up to 30 percent of people with psoriasis develop psoriatic arthritis.
If you have scalp psoriasis and are experiencing joint pain or swelling, you should speak with your dermatologist about the possibility of psoriatic arthritis. Your dermatologist may refer you to a rheumatologist for further evaluation and treatment.
Differences between psoriasis and seborrheic dermatitis
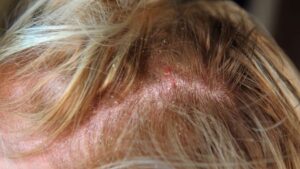
Seborrheic dermatitis is a common skin condition that causes red, or hyperpigmented, scaly patches or plaques on the scalp. It is often referred to as “dandruff,” but can be more severe that flakes in the hair.
While seborrheic dermatitis and scalp psoriasis share some symptoms, there are some key differences between the two conditions.
The scale of seborrheic dermatitis tends to be be yellow or brown and more oily than that of scalp psoriasis. The plaques are not as sharply demarcated as those of psoriasis and less commonly extend past the hair line.
Seborrheic dermatitis commonly occurs on the face particularly around the eyebrows and nose. Other common areas where seborrheic dermatitis appears is in the ears, bearded areas, the sternal chest, upper back and sometimes the armpits.
Psoriasis is less likely to occur on the face.
Differences between Scalp Psoriasis and Atopic Dermatitis
- See our Eczema Page for more information on atopic dermatitis and eczema.
Atopic dermatitis, also known as eczema, is a chronic skin condition that is characterized by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin.
Eczema can affect any part of the body, including the scalp.
In infants, it often appears on the face and scalp, while in adults it may also appear on the neck, behind the ears, and on the scalp.
People with atopic dermatitis may also experience other symptoms such as red or brownish-gray patches, skin thickening, and blisters that may ooze or crust.
Atopic dermatitis can be managed with topical treatments such as emollients, corticosteroids, and other medications. Phototherapy, oral steroids, and biologics may be used in more severe cases.
Atopic dermatitis, usually starts in infancy whereas psoriasis usually starts in adulthood.
While psoriasis commonly occurs on the extensor surfaces of the elbows and knees, atopic dermatitis characteristically occurs in the skin folds on the other side of the elbows and knees.
Psoriasis plaques tend to be well-demarcated with thick, silvery scale. Atopic dermatitis plaques tend to be ill-defined in shape with less thick scale
What Kind of Doctor Should I See?
If you suspect that you have scalp psoriasis, you should see a board-certified dermatologist like Dr. Strachan at Aglow Dermatology. She can diagnose scalp psoriasis by examining your scalp, the rest of your body, and taking a biopsy if necessary. They can also recommend the best treatment options for your particular case. Schedule a consultation with our Manhattan dermatologist here!



